本文是一篇英语论文,笔者认为不同句型的选择可以反映教师不同的言语行为。可以发现,教师使用(You)、VP(please)或祈使句非常简单易懂,但过度使用带有命令语气的句子会影响师生之间的互动,不利于学生的语言学习,挫伤学生的积极性。
Chapter One Introduction
1.1 Background of the Study
At present, English classroom is the major and important place for students to learn English, and teacher talk plays a leading role in classroom teaching (Kang and Cheng, 2011), because teacher discourse is not only a tool for teachers to make the teaching plan, but a vital medium for students to acquire language (Nunan, 1991). Meantime, the quality and quantity of teacher talk are also regarded as one of the decisive factors for the success or failure of classroom teaching (Hakansson, 1986), as shown above, researches on teacher discourse is of great value.
Teacher directions, as a vital part of teacher talk, have a unique impact on students’ language acquisition, and effective directions can produce better teaching behaviors. To be more specific, it is conducive to stimulating students’ learning motivation, enable students to actively participate in classroom activities, improve the effectiveness of classroom teaching, which contribute to students’ language acquisition. Therefore, it makes sense to study English teacher directions.
From the current research situations of English teacher directions abroad and in China, foreign educational researchers started relevant researches earlier. And domestic scholars have gradually realized the importance of teacher directions, and they have obtained certain achievements. But there are still some deficiencies, such as mechanical repetition and ambiguous reference of teacher directions (Yang, 2017; Liu, 2018 & He, 2019).
1.2 Research Significance of the Study
As mentioned above, teacher directions can effectively promote classroom teaching, because it is an important tool for teachers to impart knowledge and organize teaching. Relevant studies have attracted a series of attentions, such as the structural form of teacher directions (Guo, 2005) and pragmatic functions (Liu & Zhang, 2010). Although there have been many previous studies on higher education teacher directions, the research on English teacher directions in the high schools is still limited, especially directions of English teachers in Xinjiang senior high schools. This paper studies the teacher directions between novice teachers and experienced teachers, which will be a reasonable supplement to this field.
Based on collecting and analyzing the data from recording and interview, it can reflect the characteristics of teacher directions between novice and experienced teachers. And it can also find some ways of optimizing teacher directions, which is very valuable for pre-service teachers and in-service teachers on promoting the smooth progress of classroom teaching and improving students’ language acquisition to some extent. Therefore, the significance of this study can be explained from theoretical and practical parts.
Chapter Two Literature Review
2.1 Key Concepts
Through the comparative study of between novice and experienced teachers, it can provide a good reference for novice teachers. To some extent, the comparative study can effectively shorten the gap between the two types, and have a great impact on novice teachers’ future development. In addition, teacher directions play an indispensable role in professional development, second language acquisition and foreign language education. Therefore, this section presents the key concepts, including the definition of novice and experienced teacher, directions and teacher directions, teacher directions of types, forms, functions and strategies. Specific details are as follow:
2.1.1 Novice and Experienced Teacher
As for the criteria of novice teacher and experienced teacher, scholars and educational researchers abroad and in China both have different opinions on them. There are some very typical definitions about novice and experienced teacher, whose definitions have certain social satisfactions.
The definition of “novice teacher and experienced teacher” originated from the relevant research on the teacher development stages based on Fuller’ (1969) “teacher concern questionnaire”, which initiated theoretical investigation on faculty professional development. Berliner (1988), from American Association of Colleges for Teacher Education, demonstrated the characters of five stages of skill development in teachers, which are novice, advanced beginner, competent teacher, experienced teacher and expert teacher. Additionally, he also recommended that novices can become experienced teachers through three to four years of classroom teaching. However, most teachers enter the stage of experienced teachers in the fifth year, and only a few teachers can continue to develop into expert teachers.
2.2 Key Theories
This part presents the key theories aiming for the comparative study of the two groups of teachers, which supports for analyzing teacher directions from two aspects: how to promote teacher professional development and students’ language acquisition which means students can achieves their ultimate goals by using language. The following are three key theories: the first one is speech act theory which can be guided teachers how to achieve teaching objectives through teacher directions; the second one is comprehensible input hypothesis and third one is interaction hypothesis which refers to promote students’ language acquisition which makes students gradually acquire language through teacher directions.
2.2.1 Speech Act Theory
This section can be divided into three parts, including an overview of speech act theory, its classifications and indirect speech act.
Firstly, it was first proposed by British linguist Austin. In 1962, Austin published his book which the name is How to Do Things with Words. And in this book, utterance and action are closely linked, to be more specific, behaviors can be governed by language. In communication process, what people said is not just literal meaning, but expressing their intentions they want to achieve. In other words, people’ utterance is used to perform the certain intentions which can be realized through verbal communication. Therefore, Austin regarded this kind of behavior as a speech act, and then developed into speech act theory. It is obviously that what people said contains not only surface meaning, but also deep meaning.
Chapter Three Research Design ................................ 28
3.1 Research Purposes .............................. 28
3.2 Research Questions .............................. 28
3.3 Research Participants .................................... 28
Chapter Four Results and Discussion ................................. 36
4.1 The Similarities and Differences in the Use of Teacher Directions between Novice and Experienced Teachers............... 36
4.1.1 The Similarities and Differences in the Types of Teacher Directions between Novice and Experienced Teachers .................... 36
4.1.2 The Similarities and Differences in the Forms of Teacher Directions between Novice and Experienced Teachers ......................... 38
Chapter Five Conclusion .................................... 54
5.1 Major Findings ............................................ 54
5.2 Implications of the Research ....................................... 55
Chapter Four Results and Discussion
4.1 The Similarities and Differences in the Use of Teacher Directions between Novice and Experienced Teachers
4.1.1 The Similarities and Differences in the Types of Teacher Directions between Novice and Experienced Teachers
Different teacher directions in English classroom have different effects on students’ learning. Searle (1969) and Ur (1996) pointed out that directions, as a speech act, can be divided into direct and indirect speech act. Direct speech acts and indirect speech acts can also be distinguished in the basis of the relationship between forms and functions of Discourse (Yule, 1996). According to this classification standard, direct speech act and indirect speech act need to be realized through different discourse forms. On the basis of previous studies, Guo (2005) discussed the discourse forms of direct speech act and indirect speech act.
Combined with the collected data, based on Guo’s division of teacher directions, this study made some modifications to make it consistent with the investigation and research of this study, and used the selective coding method in the qualitative research to encode, count and analyze the teacher directions for the sake of making a more reasonable and more detailed analysis.
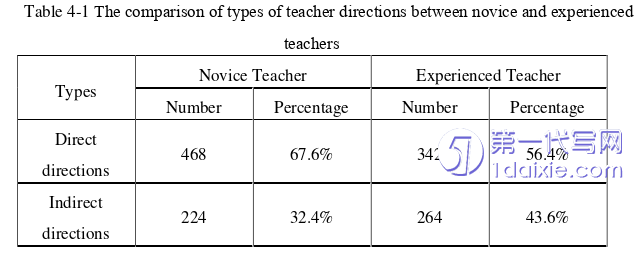
In the basis of the types’ classification of teacher directions, the comparative data between two groups of teachers are as follows:
Chapter Five Conclusion
5.1 Major Findings
This study explored a comparative study between novice and experienced teacher in the use of types, forms, functions and strategies of teacher directions based on the data collection ways of recording transcription and interview. In addition, through interviews with novice teachers, experienced teachers and their students, it can be found factors leading to the differences in the use of teacher directions between two types of teachers.
Firstly, in terms of types of teacher directions, novice teachers and experienced teachers tend to use direct directions with lower level of politeness. However, experienced teachers use more indirect directions than novice teachers. Besides, the experienced teachers pay more emphasis on the psychology of students and focus on creating a relatively relaxed and harmonious English classroom atmosphere.
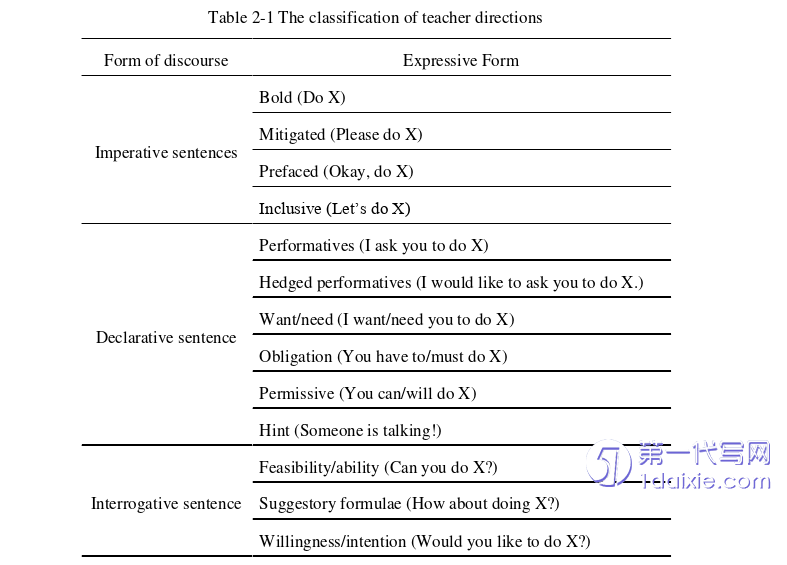
Secondly, on the aspect of forms of teacher directions, both two types of teachers tend to use the construction of (You) VP (please) or imperative sentence, which is used most frequently in direct directions. In addition, the use of declarative sentence + tag questions are less between two types of teachers. Novice teachers and experienced teachers have certain differences in the use of (You) VP (please), ellipsis and “wh-questions.” Novice teachers use more the structure of (You) VP (please) than experienced teachers. In the meantime, novice teachers also use more ellipsis than experienced teachers, while experienced teachers use more the structure of “wh-questions” or interrogative sentence than novice teachers.
The choice of different sentence forms can reflect on teachers’ different speech acts. It can be found that teachers use (You) VP (please) or imperatives in that it’s extremely simple and comprehensible, but excessive use of sentences with a tone of command can affect the interaction between teachers and students, which is not conducive to students’ language learning and frustrate students’ enthusiasm. As for ellipsis, it is obvious that young teachers want to establish authority, so students have to accept teachers’ arrangements passively. However, this way can affect student’ interest in learning. Teachers cannot mobilize students’ classroom enthusiasm, which is not beneficial to students’ language acquisition. The last one is about the interrogative sentences or “wh-questions”. Students said that they would prefer teacher directions with enlightening interrogative sentences than the directions with repetitive machinery.
reference(omitted)
