Chapter One Introduction
1.1 Background
Listening comprehension, as one of the four skills of learning foreign language, used tobe considered as a language skill with no need for any special education and learners simplycan passively acquire it, therefore, in foreign language teaching and learning it can not getenough attention. However, people found that when Chinese students had the considerablereading ability, they are distressed in the condition that they are far away from the level ofnormal communication. So, thereafter, with the development of the language acquisitionresearch, people gradually change the point of view that listening does not need education.Listening comprehension, as a basic language skill, is getting more and more attention fromforeign language world. At the same time, educational and psychological researchers at homeand abroad have realized that the basic goal of education is to make students becomeindependent, autonomous and high-efficient, and gradually shift the research emphasis frompast teacher-centered teaching method to student-centered now, and from traditional teachingmethods to the scientific methods. Although research on listening comprehension becomesmore and more, most of the research subjects are college students and students in juniorschool are seldom involved. Some researchers believe that listening comprehension hasbecome the basis for second language beginners to acquire language according to secondlanguage acquisition theory.Rost (1991) pointed out that listening plays an important role in language lab because itprovides inputs for learners. Learning is not possible for lack of comprehensive input. Latestnew curriculum standard of middle school promulgated by ministry of education has made theconcrete request,"... to enhance student's study interest, cultivate students' positive attitudetowards English learning and develop the confidence to learn English...... to help studentsdevelop good study habits, master effective learning strategies and enhance students'autonomous learning ability and cooperation spirit ".
………
1.2 Objective
In order to improve the situation above, this paper sets a goal to investigate theeffectiveness of the meta-cognitive awareness training on the performance of junior students’listening comprehension.Students in the second year of junior high school were chosen, not only because they hadexperienced listening practice to a certain extent, but also the result may help them meetlistening requirement of “Junior Middle School English Curriculum Standard (2011 revision)”and benefit them in their long-time future listening study by providing meta-cognitiveguidance. The general procedures are as follows:First of all, the author designed a questionnaire by borrowing the latest meta-cognitiveawareness listening questionnaire proposed by Vandergrift & Goh (2006), selecting items andputting them in order, and did a questionnaire survey on students, and made them have alistening pre-test. Then, the author analyzed correlation between meta-cognitive awarenessand listening achievements with the first questionnaire survey result and pre-testachievements, and found low-score students’ meta-cognitive problems in listening process,including problem-solving, planning and evaluation, personal knowledge and directedattention, by which he suggested having listening meta-cognitive training on low-scorestudents. Finally, the author confirmed with a listening post-test and a second questionnairesurvey that listening meta-cognitive awareness training of the four aspects could effectivelyimprove low-score students’ listening level.
………
Chapter Two Literature Review
2.1 Abroad
Christine Goh (1997) found that learners have strong meta-cognitive awareness and theyunderstand the learning process and the requirements of listening and know simulative andhindering factors to listening comprehension. The meta-cognitive awareness observed in theprocess of listening comprehension could be divided into three categories: subject knowledge,task knowledge and strategy knowledge. Goh classified the strategy knowledge induced fromdiary into three categories: (1) strategies contribute to understanding and memory: the visualclues (such as pictures, slides and body language, etc.), activate the text knowledge from thetitle, ignorance of the unfamiliar words, notes, identify signal words, identify thepronunciation and intonation characteristics, guess or speculate, pay attention to repeat,imagination of discourse background or speaker, interpret with the existing knowledge,request the speaker to repeat, etc.; (2) strategies to improve listening competence: talk withgood oral speakers frequently; listen to English varieties and local accent, listen to all kinds ofmaterials, enlarge vocabulary, improve the listening skills, listen to different input, be familiarwith word’s pronunciation and understand speech change, listen to materials you areinterested in and check understanding according to film subtitles; (3) strategies not alwayseffective: speculate and guess the meaning of the words and phrases, using existingknowledge, request the speaker to repeat, read film subtitles, etc.
………..
2.2 Domestic Research
Lin Qiong (2002) carried out a study on unsuccessful listeners in the "second languagelistening comprehension not successful meta-cognitive study" and drew the conclusion that, inthe second language learning process, successful learners’ listening comprehension is relatedto the success of their monitoring ability. That is to say, effective English listeningcomprehension needs learners’ higher meta-cognitive ability.Zhong Lan (2007) carried on the investigation on learners’ English listeningmeta-cognitive awareness situation in the "English listening meta-cognitive awarenessresearch" and the conclusion is: any significant correlation between of the degree of theparticipants' listening meta-cognitive awareness and listening comprehension ability does notexist. English majors’ relevant relationship between listening meta-cognitive degree andlistening comprehension is significantly different to non-English major students’.Chang Le (2008) studied on the correlation of meta-cognitive awareness and listeningscore in the "college English learners' meta-cognitive awareness and hearing resultco-relational study", he concluded: meta-cognitive awareness and listening achievementswere positively correlated.
…………
Chapter Three Research Methodology..... 11
3.1 Research Questions ..... 11
3.2 Subjects ............... 11
3.3 Instruments .......... 11
3.4 Procedures ........... 12
3.4.1 Before the Experiment ...... 13
3.4.2 During the Experiment ...... 13
3.4.3 After the Experiment ......... 14
Chapter Four Results and Discussion....... 15
4.1 Results of the First Questionnaire Survey and Pre-test....... 15
4.2 Results of Second Questionnaire Survey and Post-test....... 19
Chapter Five Conclusion.......... 21
5.1 Findings............... 21
5.2 Implications......... 22
5.3 Limitations .......... 23
5.4 Recommendations ....... 23
Chapter Four Results and Discussion
4.1 Results of the First Questionnaire Survey and Pre-test
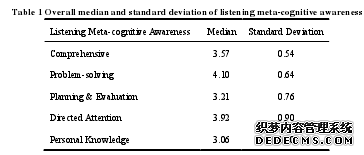
Table 1 shows the overall average number, standard deviation of the respondents’listening meta-cognitive awareness. It uncovers that the respondents have strong secondlanguage listening meta-cognitive awareness, with a median of 3.57. Among these, themeta-cognitive awareness of solving problems is the strongest (4. 10). Next are directedattention (3.92), planning and evaluation (3.21), and personal knowledge (3.06).It can be concluded from this that junior school students have strong listeningmeta-cognitive awareness, but there exists certain difference between individuals.In order to finish listening tasks, in the listening process the respondents do reasoning todirect at the parts they didn’t understand and take other strategies such as word-guess, monitor,etc. The respondents also realized the importance of directed attention, and could adjust hisattention consciously in the listening process and could even manage in time as possible as hecould when encountering difficulties. In planning and evaluation and personal knowledgeparts, the respondents’ cognitions fall into the medium level. Before listening, the respondentshave certain consciousness prepared for the listening activity, and assess listening effectsafterwards, positively managing the listening process. Meanwhile, the respondents have clearknowledge about the listening difficulty and their self-efficacy and other aspects in secondlanguage listening.
…………..
Conclusion
Through a 3-month teaching study with listening meta-cognitive awareness trainingaimed at junior school English, the findings are as follows:5.1.1 High-score Students Have Higher Meta-cognitive Awareness than Low-score OnesThe meta-cognitive awareness includes four aspects: problem-solving, planning andevaluation, personal knowledge and directed attention.From the overall situation of meta-cognitive awareness, relevance of listeningmeta-cognitive awareness with listening comprehension level and difference ofmeta-cognitive awareness between high-score group and low-score one, it was found that thejunior school students did have strong meta-cognitive awareness with an overall average of3.57, and among these, the cognition of solving problems was the strongest (4. 10), next weredirected attention (3.92), planning and evaluation (3.21), and personal knowledge (3.06);listening comprehension level is related to listening meta-cognitive level. Besides, thereexisted a great difference of problem-solving, planning and evaluation, personal knowledgeand directed attention between the high-score and low-score learners. From all above, it wasproposed that it was worthy of making learners receiving meta-cognitive training in the fouraspects. Then an experiment was done to verify the effectiveness of listening meta-cognitivetraining.
…………
Reference (omitted)
