银行学留学作业-2008年全球金融危机对银行业的影响。本文是一篇银行学专业留学作业范文,主要内容是讲述2008年的突然冲击给全球银行业带来了大量意想不到的结果。本篇留学作业的目的是分析和评估政府为应对危机后暴露的后果而颁布的法规。因为它在恢复过程中起着至关重要的作用,在安抚纳税人情绪的同时努力保护他们的权利,比如巴塞尔协议III压力测试系统的问题。下面就一起参考一下银行学留学作业范文的全部内容。

Analyse and Evaluate the Impact of the 2008 Global Financial Crisis on the Bank Sector 分析和评估2008年全球金融危机对银行业的影响
Introduction 简介
Things were unnoticed until it happened. The sudden shock in 2008 caused large number of unexpected outcomes to the global banking industry. The purpose of the essay is to analyse and evaluate regulations that governments issued to deal with the consequences that exposed after the crisis. Since it plays a crucial role on the recovery process and calm taxpayers’ emotions at the same time try to protect their right such as the issue of Basel III stress testing system.
The global bank sector especially in western countries heavily suffered from the subprime crisis. The US mortgage-backed securities and collateralized debt obligations with initially offer higher investment return and seductive risk ratings such as Triple A products absorbed many countries’ banks to do a cross-broad investment (Zandi, 2009). Naturally, the meltdown of financial instruments would spread through the global banking industry.
全球银行业,尤其是西方国家的银行业,深受次贷危机之苦。美国抵押贷款支持证券和债务抵押债券最初提供了更高的投资回报和诱人的风险评级,比如AAA产品吸引了许多国家的银行进行跨领域投资。自然,金融工具的崩溃会蔓延到全球银行业。
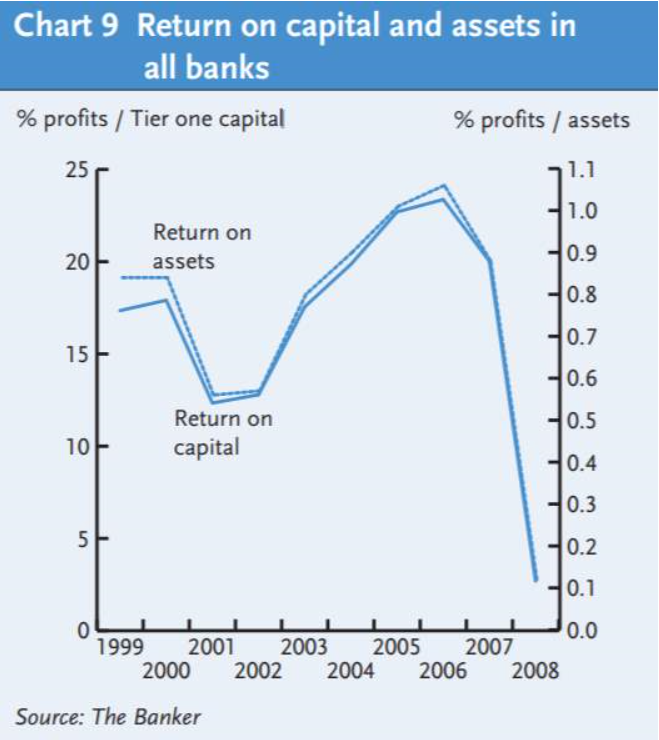
The negative impact mainly appears on worldwide banks business performance according to the credit crisis. As the table below shows the movement of ‘average global return on capital fell to 2.69% in 2008/09, from 20.02% in the previous year’ (IFSL, 2010, p.4). The characteristic of these financial instruments appears to have high leverage rate, in other words, the debt level is higher than the expected cash flow. In addition, the market value of these products does not equal to its fair value. Consequently, in Europe and the US, some banks could not afford the spread of value and went to fail such as Lehman Brother, and some banks such as JP Morgan were restructured and bailed-out by governments.
从信贷危机来看,其负面影响主要表现为对全球银行经营业绩的影响。如下表所示,“全球平均资本回报率从前一年的20.02%下降到2008/09年的2.69%”。这些金融工具的特点似乎是杠杆率高,换句话说,债务水平高于预期现金流。此外,这些产品的市场价值不等于其公允价值。因此,在欧洲和美国,一些银行承受不起价值的扩散而倒闭,比如雷曼兄弟,而一些银行,比如摩根大通,则被政府重组和救助。
The downward performance on banks raised the attention of governments and relevant regulations introduced to deal with the weakness that imposed in the financial crisis. Mishkin (2010) states that Investment banks expand on a large scale in the self-operated business of highly leveraged financial derivatives before and during the credit crunch. It is suggested that higher leverage rate usually follows with higher risk-taking, which may contribute the bankruptcy of these institutions.
银行业绩下滑引起了各国政府的关注,并出台了相关法规,以应对金融危机造成的疲软。Mishkin指出,在信贷危机之前和期间,投资银行大规模扩展了高杠杆金融衍生品的自营业务。有人认为,较高的杠杆率通常伴随着较高的风险承担,这可能导致这些机构破产。
As in the United State, in response to the great recession, the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act was issued by the Obama government (Congress, 2010). Still, the Volcker Rule proposed by Paul Volcker as a part of the Act mainly concentrates on the transform of bank sector. It offers two proposals to deal with the problems that financial institutions incurred during the crisis.
与美国一样,为了应对大衰退,奥巴马政府发布了《多德-弗兰克华尔街改革和消费者保护法案》。尽管如此,保罗·沃尔克(Paul Volcker)作为该法案的一部分提出的沃尔克规则主要集中于银行业的转型。它提出了两项解决金融机构在危机期间遇到的问题的建议。
First, limiting the scope, or controlling the speculative trading activities of banks. Volcker Rule (Congress, 2010) documents the prohibition of banks to invest in or sponsor a hedge fund or a private equity fund, or proprietary trading operation for its own interest and irrelevant to their clients. The rule aims to improve the transparency of the bank operation systems and arise the awareness of these institutions to take responsibilities. According to the policy, banks need to divide the commercial and investment sector strictly and being more cautious with the business of clients. However, critics pointed out some limitation of Volcker principle (Elizabeth, et al., 2010). As metric tools for banks to calculate the performance on investment and commercial sectors are flexible and the rule appears to vague on this part (Valladares, 2018). Thus, it is hard to trust the self-assessment result published by financial institutions. Yet, for the implementation of the rule, each bank has a transition period and grace period, and there are no specific items to restrict banks to comply with the rules (govinfor. 2010). Therefore, Volcker Rule is relatively loose and gives the possibility of companies to escape and extend the date of execution.
第一,限制范围,或控制银行的投机交易活动。沃尔克规则规定,禁止银行为自身利益投资或赞助对冲基金或私募股权基金,或自营交易业务,且与客户无关。该规定旨在提高银行运营系统的透明度,并提高这些机构承担责任的意识。根据该政策,银行需要严格划分商业和投资部门,并对客户的业务更加谨慎。然而,批评人士指出了沃尔克原则的一些局限性。由于银行用于计算投资和商业部门绩效的度量工具是灵活的,这方面的规则似乎很模糊。因此,很难相信金融机构公布的自我评估结果。然而,对于该规则的实施,每家银行都有一个过渡期和宽限期,没有具体的条款限制银行遵守该规则。因此,沃尔克规则相对宽松,使公司有可能逃脱并延长执行日期。
Second, limiting the size, ending ‘too big to fail’. Paul (2010) proposed forbidding government bailouts some troubled systemically important financial institutions (SIFIs). In addition, investment banks have undergone ownership transformations. For instance, Morgan Stanley and Goldman Sachs transfer to be regulated as commercial banks with federal government guarantees (Guardian, 2013). However, the government would not always be capable to secure SIFIs in the long-term period since the creditability of it had been suspected.
第二,限制规模,结束“太大而不能倒”的局面。Paul提议禁止政府救助一些陷入困境的系统重要性金融机构(SIFI)。此外,投资银行也经历了所有权转换。例如,摩根士丹利和高盛将被监管为有联邦政府担保的商业银行。然而,政府并不总是能够在长期内获得SIFI,因为它的信誉受到怀疑。
Compared with the US, German’s central bank Deutsche Bank still put large efforts on the business of the investment sector. Instead of following the mainstream trend to decrease the derivatives exposure, Deutsche continued to respect the high leveraged business model and high-risk financial speculation.
与美国相比,德国央行德意志银行仍在投资部门的业务上投入了大量精力。德意志银行没有跟随主流趋势降低衍生品风险敞口,而是继续尊重高杠杆商业模式和高风险金融投机。
This business model has brought considerable profits to Deutsche in the short as it accounted for 60% revenues, but in the long-term it does hurt the bank’s value. For instance, Deutsche bank cut a fifth of its global workforce especially in the investment sector to reduce the cost and ensure the daily operation (Pandey, 2019).
这种商业模式在短期内为德意志银行带来了可观的利润,因为它占到了60%的收入,但从长期来看,它确实损害了德意志银行的价值。例如,德意志银行(Deutsche bank)削减了全球五分之一的劳动力,尤其是在投资领域,以降低成本并确保日常运营。
Moreover, when comes to regulations issued on saving reputation, Deutsche Bank concentrated on the recovery of shareholders wealth and the payout ratio (Y. Biondi, I. Graeff, 2017). However, the bank did not develop a sustainable policy to maintain the stability of the stock market and the uncertainty of dividend price is tightly connected to the company’s growth, cash flow and asset liquidity. For example, the dividend per share increased significantly with €1.30 in 2001 to €4.5 in 2007 which increased by 246%, then dropped considerably by 88%, € 0.50 in 2008 and then return (Deutsche Bank, 2016).
此外,在有关储蓄声誉的监管方面,德意志银行将重点放在了股东财富的回收和派息率上。然而,本行没有制定可持续的政策来维持股票市场的稳定,股息价格的不确定性与公司的增长、现金流和资产流动性密切相关。例如,每股股息显著增加,从2001年的1.30欧元增加到2007年的4.5欧元,增加了246%,然后大幅下降了88%,2008年为0.50欧元,然后返回。
Different from Germany, the government strictly controls the investment sector on the UK. The banks in the United Kingdom are now partly or wholly owned by their government which intend to establish a much safer financial system. For instance, the largest banks ring-fence their investment department from the retail department which aim to protect retail banking sectors from other risks in the financial system and to improve the flexibility and solvability of banks (BBA, 2016). However, the ring-fencing might reduce the available activity of commercial banks and limits the variety of individual investment.
与德国不同,政府严格控制英国的投资部门。英国的银行现在部分或全部归政府所有,政府打算建立一个更安全的金融体系。例如,最大的银行将其投资部门与零售部门隔离开来,以保护零售银行部门免受金融体系中的其他风险,并提高银行的灵活性和可解决性。然而,隔离可能会减少商业银行的可用活动,并限制个人投资的多样性。
It is undeniable that these countries have actively remedy and reformed the damage caused to the banking industry after the 2008 financial crisis, but they all seem to stop at the urgent need and the effect of recovery tends to be slightly dull.
不可否认的是,这些国家在2008年金融危机后对银行业造成的损害进行了积极的补救和改革,但它们似乎都止步于迫切需要,复苏的效果往往稍显平淡。
Not only to solve problems exposed after the crunch on the bank sector, governments and authories also trying to protect the right of taxpayers. Basel III offer a global stress testing system designing to enhance bank capital requirements by increasing bank liquidity and reducing bank leverage (BIS, 2018). In other words, it works as a supervisory standard for checking whether banks have capabilities to meet another extreme situation such as a new financial crisis.
不仅是为了解决银行业危机后暴露出来的问题,政府和当局还试图保护纳税人的权利。巴塞尔协议III提供了一个全球压力测试系统,旨在通过增加银行流动性和降低银行杠杆来提高银行资本要求。换句话说,它是一种监管标准,用来检查银行是否有能力应对另一种极端情况,比如新的金融危机。
The stress testing would benefit the market participant such as taxpayers to invest in a safer environment. Firstly, stress testing forces banks to disclosure some internal information to public which reduce the opacity and information asymmetry between taxpayers (Kapinos et al., 2018). As more information be more transparent, taxpayers can keep the mindful of avoiding investing on residual financial products and make more wisely decisions. Secondly, stress testing can act as a clock to remind taxpayers when financial system appears to have a fundamentally unstable behavior. Under the period of economic and financial calm, the market would be vulnerable to huge losses and easy to fall into collapses (Kapinos et al., 2018). Hence, taxpayers would need the stress testing system to recognize the uncertainty investment portfolio and perceive the following development would not respect the current market trends. For instance, during the great recession, almost all market participants expected a higher mortgage price on the US housing market instead of the considerable devalue and nearly several companies created a stress testing to predict the movement.
压力测试将有利于纳税人等市场参与者在更安全的环境中投资。首先,压力测试迫使银行向公众披露一些内部信息,这减少了纳税人之间的不透明性和信息不对称。随着更多信息变得更加透明,纳税人可以保持警惕,避免投资剩余金融产品,并做出更明智的决定。其次,压力测试可以作为一个时钟,在金融系统似乎存在根本性的不稳定行为时提醒纳税人。在经济和金融平静时期,市场将容易遭受巨大损失,并容易崩溃。因此,纳税人需要压力测试系统来识别不确定性投资组合,并认为以下发展不会尊重当前的市场趋势。例如,在大衰退期间,几乎所有的市场参与者都预期美国住房市场的抵押贷款价格会更高,而不是大幅贬值,而且几乎有几家公司创建了压力测试来预测这种走势。
Basically, stress test would be efficient on disclosing the information and risks of bank industry. However, some scenarios would bring unmeaningful outcomes, although the risks have been revealed (Thun, 2013). For example, since Deutsche Banks’ American subsidiary passed the stress test, but it developed delinquent conducts such as money laundering (Stacey and Morris, 2019). Thun (2013) stats that the hardest barriers might be insufficient data and uncapable designer to establish a complete scenario that not only focus on the know defect, but also the foreseeing risks. The misleading from the root may directly affect the method that taxpayers supposed to follow. Therefore, the wrong guidance would be an approach that damage taxpayers’ benefits.
基本上,压力测试可以有效地披露银行业的信息和风险。然而,尽管风险已经暴露出来,但一些场景会带来毫无意义的结果(Thun,2013)。例如,德意志银行的美国子公司通过了压力测试,但出现了洗钱等违法行为。Thun指出,最困难的障碍可能是数据不足和无法胜任的设计师,无法建立一个完整的场景,不仅关注已知的缺陷,还关注可预见的风险。这种从根本上的误导可能会直接影响纳税人应该遵循的方法。因此,错误的指导方针会损害纳税人的利益。
Conclusion 结论
Governments and authorities offered regulations positively response to the negative impact fallen in the global bank industry after the 2008 financial crisis. America, Germany and the United Kingdom as typically western countries concentrated on reforming the industry rules to control and intervene the operation of investment banks’ businesses. However, the regulations would only solve the urgent need, not establishing in a sustainable development perspective. Taxpayers’ rights have also been concerned, as taxpayers blindly invested on the US mortgage, large amount of them suffered losses. Basel III stress testing works as a guidance to support market participants perceive the movement of market. Critics pointed the limitations of current stress test on inappropriately using scenarios to mislead the industry. The system needs more data and talent to continue the future adjustment.
References 参考文献
Biondi, Y. and Graeff, I. 2018. Rethinking bank shareholder equity: The case of Deutsche Bank. Accounting Forum.41(2017), pp.318-33
BIS. 2018. Stress Testing Principles. . [Accessed 19 August 2019].
Deutsche Bank. 2016. Annual Report.
Elizabeth, H., Ashley, M., Violeta, S. and Jayne, F. 2010. Bank Regulatory Reform in the United States: The Case of Goldman And the Volcker Rule. Journal of Business Case Studies. 6, p64.
Govifo. 2010. Implications of the ‘Volcker Rules’ for Financial Stability.
Kapinos, P., Martin, C. and Mitnik, O. 2018. Stress Testing Banks: Whence and Whither? Journal of Financial Perspectives. 5(1), pp 3-4.
Kay, J. 2016. Don’t Always Believe A Balance Sheet. Financial Time.
Stacey, K. and Morris S. 2019. US Fed quizzes Deutsche on ‘bad bank’ plans. Financial Times.
Maslakovic, M. 2010. IFSL Research: Banking 2010.
Mishkin, F. 2011. Over the Cliff: From the Subprime to the Global Financial Crisis. Journal of Economic Perspective. 25(1), pp.49-70.
Pandey, A. 2019. Deutsche Bank’s uncertain road to recovery. DW.
Thun, C. 2013. Stress Testing: European Edition. The Journal of Risk Perspectives. 1, pp 24-39.
Valladares, M, R. 2018. BankThink Getting the Volcker Rule right may be a waste of time. American Banker. [Online]. 15 August. [Accessed 1 September 2019].
留学作业总结到2008年金融危机后,各国政府和当局对全球银行业的负面影响做出了积极回应。作为典型的西方国家,美国、德国和英国致力于改革行业规则,以控制和干预投资银行业务的运营。然而,这些规定只会解决紧迫的需求,而不是建立在可持续发展的角度。纳税人的权利也受到了关注,因为纳税人盲目地投资于美国的抵押贷款,他们中的很多人蒙受了损失。巴塞尔协议III压力测试作为一种指导,支持市场参与者感知市场的运动。批评人士指出,当前压力测试的局限性在于不恰当地使用情景误导行业。该系统需要更多数据和人才来继续未来的调整。
本站提供各国各专业留学作业写作指导服务,如有需要可咨询本平台。
