本文是一篇英语论文,研究者针对阅读教学提出了几点建议,教师要不断提升自身的教学水平和知识储备,在阅读教学中充分调动学生的积极性和主动性。同时在日常的教学工作中,重视对学生思维品质的培养。
Chapter 1 Introduction
1.1 Background of the Research
In April 2022, the Ministry of Education issued the newly revised 2022 version of compulsory education curriculum standards. The starting point and foothold are to cultivate students with ideals, abilities, and responsibilities in the new era. As the essence of the value of curriculum education, core literacy is reflected in the students' gradual construction of correct values, necessary characters, and key abilities that are consistent with lifelong development and social progress through systematic curriculum learning. It is particularly worth mentioning that the English course covers many dimensions such as language ability, cultural awareness, thinking quality and learning ability in cultivating students’ core literacy. These four aspects are intertwined, integrated and interactive, and jointly promote the comprehensive development of students.
But for the cultivation of students' thinking quality, there are still some problems in the current teaching. In daily teaching activities, teachers do not pay enough attention to the cultivation of students' thinking quality, ignoring the subjectivity and development of students. Students are developing people. For students in junior high school, it is the critical period for the development of thinking quality. Teachers should seize the critical period and cultivate students' thinking quality. Second, teachers' Cultivation of students' thinking quality is not systematic, and they do not integrate systematic cultivation into teaching activities.
1.2 Purposes of the Research
The research focuses on experimentally enhancing the thinking skills of students in junior high school English reading classes. By examining and investigating open questions in these classes, the study aims to understand how these challenges affect students' thinking abilities. Ultimately, the findings offer valuable insights for English reading instruction.
Chapter 2 Literature Review
2.1 Thinking Quality
2.1.1 Definition of Thinking Quality
First of all, it is very important for this research to define the quality of thinking. As for the definition of thinking quality, many scholars at home and abroad have their views and opinions and have defined thinking quality from different angles.
Soviet psychologist Smirnov (1956) elaborated on the quality of thinking in his book Psychology edited in 1956. He pointed out that although thinking activities generally follow certain rules, different individuals show unique characteristics in thinking. These unique thinking qualities include the breadth and depth of thinking, reflecting the scope and depth of people's thinking, flexibility and independence revealing people's ability of flexibility and independent thinking when solving problems. These individual qualities together constitute the multifaceted nature of people's thinking and provide a rich perspective for us to understand human thinking activities.
American psychologist Guilford was the first to put forward the concept of thinking quality in 1959, and based on the three-dimensional model of the intellectual structure of thinking, he focused on the characteristics of thinking quality, pointing out that the core of creative thinking is divergent thinking.
2.2 Open Question
2.2.1 Definition of the Open Question
Open questions are widely used in the current classroom, especially in science subjects, such as mathematics, physics and chemistry. Open questions are called ill-structured problems in educational psychology. Usually, a problem always contains three elements: conditions, objectives and approaches. In general, the problems that students solve are problems with clear conditions and objectives, and the problems with relatively simple ways to solve problems are called well-structured problems. If the conditions and objectives are clear, there are multiple ways to solve the problem, or only one of the conditions and objectives is known, and the solution is completely unknown, the problem structure is incomplete and the idea is not clear, which is the problem of poor structure. However, at present, there is no authoritative definition of open problems, and researchers have not yet reached a unified view. So, what is the open question?
Becker (1997) called the question with multiple correct answers as an open question. When students are exposed to open questions, they are only solving open questions when they focus on the exploration of different solutions in the process of problem-solving, rather than looking for the answer to the question. It is emphasized that the key to problem-solving is not to get several answers, but the method to get these answers. Therefore, the openness of open questions lies in the solution, not the answer.
Chapter 3 Research Design and Implementation ..................................... 25
3.1 Research Questions ............................. 25
3.2 Research Subjects ............................ 26
3.3 Research Instruments ............................... 26
Chapter 4 Results and Discussion ................................... 37
4.1 Analysis on the Current Situation of Teachers' Use of Open Questions in Teaching and Students' Thinking Quality ........................................ 37
4.1.1 The Current Situation of Teachers' Use of Open Question in Teaching .................................. 37
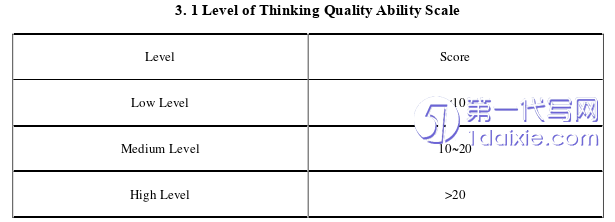
4.1.2 The Current Situation of Student’s Thinking Quality ................ 39
Chapter 5 Conclusion ............................... 67
5.1 Major Findings .............................. 67
5.2 Limitations of the Research .......................... 69
5.3 Prospects of the Research ................................ 69
Chapter 4 Results and Discussion
4.1 Analysis on the Current Situation of Teachers' Use of Open Questions in Teaching and Students' Thinking Quality
This section is an analysis of the current situation. It aims to solve the problems that what is the current situation of teachers using open questions to teach in junior high school English reading class and what is the current situation of students' thinking quality. Mainly including interview analysis and questionnaire survey analysis.
4.1.1 The Current Situation of Teachers' Use of Open Question in Teaching
In order to understand the current situation of teachers' teaching with open questions, the researcher interviewed teachers. The teachers who participated in the interview were all English teachers of the grade, a total of 6 teachers, including older teachers and new teachers who had just started teaching. There are seven questions in the interview, four of which are about the current situation of teachers' use of open questions in teaching. The following is an analysis of the teacher interview.
Chapter 5 Conclusion
5.1 Major Findings
Based on the Zone of Proximal Development Theory and Bloom's Classification Theory of Educational Objectives, this study carried out an empirical study of open questions in junior high school English reading class on the improvement of students' thinking quality, aiming to explore the following three problems:
1.What is the current situation of teaching with open questions in junior high school reading class? What is the current situation of students' thinking quality?
2. How to use open questions to improve students' thinking quality in junior high school English reading class?
3. What specific aspects of students' thinking quality have improved after the implementation of open question reading teaching experiment?
After a semester of teaching experiments on eighth-grade students in a middle school in Luoyang, the main findings are as follows.
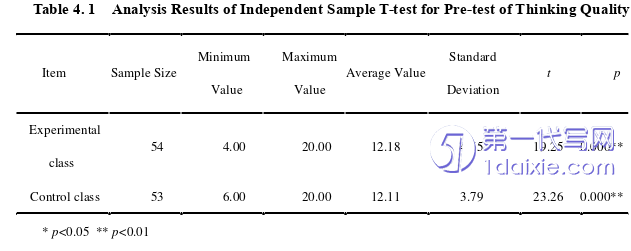
Firstly, through the questionnaire survey and the interview analysis of students and teachers, it can be seen that in the current situation of teachers' use of open questions in junior high school English reading class, most teachers use open questions in reading class, but the frequency of use is not high, and the design of open questions is not perfect; In terms of the current situation of students' thinking quality, the level of students' thinking quality is not high, which is generally at the medium level, and the level of students' thinking quality is not different. At the same time, in all dimensions of thinking quality, students' level of critical thinking and logical thinking is higher than that of innovative thinking. In addition, students lack systematic training on improving their thinking quality.
reference(omitted)
