Chapter 1 Introduction
1.1 Background of the Present Study
To doresearch on it, the most effective measurement of working memory capacity, calledworking memory span came up. Since working memory owns the processing function, many studies about therelationship between working memory capacity and second language reading comprehension have been done, with focus on its effect on sentence comprehension.And the results show that readers of low working memory capacity are weaker indealing with the complex syntactic structures. Therefore, it takes them more time toread those sentences, but the efficiency is lower than those of high working memorycapacity. Besides, some studies about the relationship between working memorycapacity and listening comprehension have been done before. However, the studiesabout the relationship between working memory capacity and second languagewriting are very limited. Among them, the most foreign representative ones include Amodel of working memory capacity in writing (Kellogg, 1996), Working memorycapacity and L2 writing performance (Bergsleithner, 2010); the representative ones athome contain the Empirical Study on the Components of Working MemoryParticipating in Written Language Output of Second Language Learners (Luo&Wang, 2011) and the Effect of Working Memory Capacity on Written LanguageProduction of Second Language Learners (Yi & Luo, 2012). Therefore, the studiesabout the relationship between working memory capacity and written languageproduction are still very not enough.
……….
Overall Structure of the Thesis
The thesis is made up of five chapters. Chapter one is the introduction of thestudy, including the background, significance and the overall study of the thesis.Chapter Two reviews all the relative literature theories, where theories of workingmemory and language production and the previous studies are introduced in details.Chapter Three is concerned with the empirical study, in which research questions,subjects, research procedure, data collection and analysis are introduced. ChapterFour presents the statistical results as well as the explanations and discussions.Chapter Five makes a conclusion of the whole study, summing up the major findings,and giving the pedagogical implications. The limitations of the study and somesuggestions for the further study are also addressed.
……….
Chapter 2 Literature Review
2.1 Theories on Working Memory
Since the study is about the effect of working memory capacity on Englishwritten production, the theories on working memory including working memory inhuman information process, functions of working memory and working memorymodels are reviewed in the this chapter. As Carroll (2000) suggested, according to the information processing system,environmental information can be processed through a set of mental structuressuccessively. This process includes encoding, storing and retrieving. It involves manyactivities, such as remembering numbers, solving mathematical problems and usinglanguage. A general model about this process is shown in Figure 2.1The model is made up of three mental structures and a series of processes inwhich information can be dealt with from one structure to the next one.As the model suggests, the incoming sensory information, first of all, is kept inthe structure of sensory stores in the state, which is literal and unanalyzed. Then theincoming information will be identified whether relevant to the current activity by theinformation from permanent memory. If relevant, the information comes to the nextstructure, the working memory, in which the information can be held for longerperiods. And during this time, the identified information is used to deal with thesimple acts, such as solving mind problems. When the acts are finished, some of theolder information can be processed into larger units by chunking while otherinformation which is useless to next acts is lost. Only a small part of the informationcan be transmitted to permanent memory.
……….
2.2 Written Language Production
As for the process of writing, there are two main assumptions. They are Hayesand Flower’s theory of written production and Kellogg’s theory of written production.Next the two theories will be introduced in detail.2.2.1.1. Hayes & Flower’s AssumptionsIn 1980, Hayes and Flower together published the paper Identifying theOrganization of Writing Processes, and how the cognitive factors involve in writingprocesses was analyzed in details. In this paper, written production can be divided intothree stages: planning, translating and revising. Planning is the first sub-processamong writing, when writers can build an internal representation of the knowledgethat will be used in writing. However, during this stage, the internal representation isnot specific but abstract, which still cannot be written in language but stays as visualor perceptual code. And the planning process also is made up of a great manyprocesses, of which the act of generating ideas is the most important one. The ideassometimes are organized and developed well enough to form the final standardwritten production; or the ideas may be only fragmentary, unconnected thoughts, likethe stream of consciousness. If the structure of ideas is not well- formed, anothersub-process, organizing, will help writers make senses. Besides, goal-setting is also amajor sub-process of planning throughout the whole writing. The goals that are setcan result in idea-generating, and more complex goals can combine content andpurpose together.
……….
Chapter 3 Methodology...... 27
3.1 Research Questions.... 27
3.2 Subjects.... 27
3.3 Instruments .... 28
3.3.1 English Working Memory Span Task ...... 28
3.3.2 Tests of English Writing......... 30
3.4 Research Procedure ......... 32
3.4.1 Pilot Study...... 32
3.4.2 Experiment..... 33
3.5 Data Collection and Analysis ...... 32
Chapter 4 Results and Discussion ....... 37
4.1 Results ..... 38
4.2 Discussion...... 47
Chapter 5 Conclusion ......... 53
5.1 Major Findings .... 53
5.2 Pedagogical Implications....... 54
5.3 Limitations of the Study ........ 56
5.4 Suggestions for Further Research......... 57
Chapter 4 Results and Discussion
4.1 Results
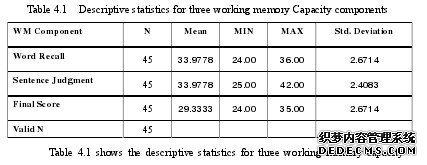
After dealing with the data, we get the results. Since participants were informedthat the scores of the writing task is related with the final scores of this semester, allthey treated this writing task seriously. Through valuing the whole compositions, noone digressed from the subject. Therefore, all the results are valuable for the study.The whole process advances be the means of the software Statistical Package forSocial Science (SPSS, the 10.0 version). When analyzing the results of data, theresearcher selected the probability as the critical value. The 4.1 Table of descriptive statistics concerningworking memory capacity contains the mean (measuring the central tendency of data),the minimum, the maximum and the standard deviation (measuring the dispersion orspread of the distribution). Besides, Valid N refers to the total number of participantswho were involved in the study.
………..
Conclusion
The paper has studied whether working memory capacity affects writtenlanguage production. The all the results of this study indicate that learners’ workingmemory capacity can influence the written language production, and the mainfindings are listed as follows:
1. Generally speaking, the individual differences of working memory capacityinfluence written language production’s accuracy obviously. Besides, the writtenlanguage production of learners with high working memory capacity is more accuratethan that of learners with low working memory capacity.
2. Individual differences of working memory capacity affect written languagewritten language production’s fluency but not too much. But for learners of lowworking memory capacity, the influence is relatively obvious.
…………
Reference (omitted)
