Chapter One Literature Review
1.1 The Concept and Characteristics of CI
Consecutive interpretation (or consecutive interpreting), a typical type of interpretation,refers to a series of acts: the interpreter begins his/her interpreting with the help ofnote-taking and memorizing, after the source language speaker has finished his/her speakingof a complete paragraph or a part of the source speech. When an interpreter translates thesource language into the target language, he/she should cover all the details rather than give asummary. Nowadays, consecutive interpretation is widely used in different occasions, suchas conference, speech, negotiation, interview, and banquet, and covers varied subjects, suchas diplomacy, politics, business, science and technology, medical, etc.The characteristics of consecutive interpretation are as follows:First, the time for listening and sentence-organizing is limited in CI. As known to all, CIis an impromptu activity. On one hand, speakers’ speeches are spoken once only. Only insome special cases, the interpreter can listen to the source speech for more than once. Forexample, when an interpreter misses some of the information, he/she can ask the speaker torepeat what he/she has said. In fact, this kind of cases seldom happens, and what’s more, evenwhen it happens, the speaker is likely to repeat some words or a small group of sentencesrather than the whole paragraph. On the other hand, consecutive interpretations requireinterpreters to give their translations right after the speakers finish their speaking (sometimesa few seconds of delay is allowed). Therefore, interpreters have to understand what thespeakers want to express and organize the information in the target language in limited time.
………..
1.2 AThe research subjects are comprised of two classes with the total number of 74students majoring iThe research subjects are comprised of two classes with the total number of 74students majoring ivoiced) that can be observed.When giving a speech, some kind of short pauses are necessary because they can help theunderstanding, such as the short inter-lexical pauses and the short pauses between twosentences which help to separate the two contiguous words or sentences. These kinds ofpauses are less easy to be perceived by the listeners. According to some linguists, “Pauses aremore easily perceived if their duration is around 200-250ms.” (Goldman Eisler, 1968;Grosjean and Deschamps, 1975) Some linguists have different opinion, such as longer than250ms. (Mead, 2002) The silent pauses analyzed in this paper are all longer than 250ms.According to psycho-linguistics, there are two types of pauses: silent pauses and filledpauses. The former refers to the brief silence that can be observed in the speech signal.According to the linguist Brigitte Zellner, “Such pauses may be produced in conjunction withan inspiration, swallowing, any laryngo-phonatory reflex, or a silent expiration.” (BrigitteZellner, 1994) The latter refers to the unnecessary voiced sections filled in the speech signal. Most of the linguists discuss these kinds of pauses in English and French, and they come to aconclusion that the filled pauses are “drawls, repetitions of utterances, words, syllables,sounds, and false starts”. (Grosjean and Deschamps, 1975; Bloodstein, 1981)
………………….
Chapter Two Research Design and Data Collection
2.1 Research Design
In order to fully analyze the causes of pauses in CI, this paper combines two types ofresearches: questionnaire and experiment. The reasons why the paper chooses to use these 2types of research methods are that: first, the questionnaire can collect the ideas of theparticipants, that is to say, it can collect different ideas, and give a whole picture of it insteadof only cover the author’s limited ideas; second, the experiment, which simulates the wholeaction of CI, can give a comparison (compare with the results of the questionnaire) and sometypical examples for the analysis. As some of the causes can hardly be realized by interpretersin daily practice, the experiment can help the paper to discover and analyze them effectively.The questionnaires are given to the participants before the experiment. The reasons areas follows:First, try to cover all the details. In case the author’s opinions are limited, this papergives the questionnaire first, in order to collect different opinions.Second, compare the results. This paper compares the results of the questionnaire withthe result of the experiment, in order to find out the differences between the two sides.
………
2.2 Data Collection and Findings
54 copies of the questionnaires are given to the 54 MTI students (including 24 grade 2MTI students and 30 grade 1 MTI students), while 52 valid ones are received (including 22copies from grade 2 MTI participants and 30 copies from grade 1 MTI participants). Thedata and findings of the questionnaire are listed in the following charts and histograms.Chart 1 and Chart 2 show the occurring frequence of pauses in CI. From the twocharts it can be seen that the occurring frequence of the two groups are nearly the same.The quantity of the participants who choose “regular” (16 in grade 1; 12 in grade 2) isslightly more than the participants who choose “not regular” (14 in grade 1; 10 in grade 2),and no one chooses “never”. This shows that all the participants admit that they makepauses in CI.
Chapter Three Cause Analysis of Pauses in CI. ..... 21
3.1 At Information Input Stage ..... 21
3.2 At Note-taking Stage ........ 24
3.3 At Information Output Stage ........ 27
3.4 Psychological Causes ....... 29
3.4.1 Environmental Stress......... 30
3.4.2 Interpreters’ Mental Pressure......... 30
3.5 Other Causes......... 31
3.5.1 Slip of Tongue........ 31
3.5.2 Poor Language Habit ......... 32
Chapter Four Countermeasures ...... 33
4.1 Skills Training and Accumulation of Necessary Knowledge ....... 33
4.2 Sufficient Preparation ....... 34
4.3 Psychological Quality Improvement ........ 34
4.4 Other Measures..... 35
Chapter Four Countermeasures
4.1 Skills Training and Accumulation of Necessary Knowledge
First, interpreters should take more translation training. The translation skills cangreatly help the interpreters in interpreting. Because when an interpreter is familiar with thetranslation skills, he/she can apply them whenever needed.Second, interpreters should take more listening practices. Listening comprehension isvery important to the input stage of CI. It will help the improvement of input quality if onetakes enough listening practices. And what’s more, listen to the original listening materialsspoken by native speakers can help interpreters to get familiar with the native way ofthinking and expressing. Besides, interpreters also need to take more exercises on differentaccents.Third, interpreters should take more note-taking practices. When doing the practice, thefirst task for interpreters is to find out some effective and appropriate symbols. The secondtask is to get familiar with the symbols. In this case, it will save the interpreters’ time andenergy in doing consecutive interpretation.
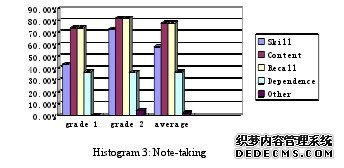
…………
Conclusion
As one of the main factors which cause disfluency in CI, improper pauses not only leavethe audiences a bad impression, but also tarnish the quality of the outcome. Therefore, it isnecessary to find out the causes of pauses in CI and give some effective suggestions. Thispaper analyzes the causes with the help of related questionnaire and experiment.The main findings of the related questionnaire and experiment are: first, silent pausesare usually companied by filled pauses; second, pauses occur more frequently at thebeginning sentences of each speech; third, for most of the cases, the place where a pauseoccurs is not necessarily where the interpreter has a problem (the reason is that the interpreterhas to fore-think the next couple of words, or even the following sentences, whileinterpreting the current part); fourth, pauses are likely to be produced when there is a number(especially when the number is complicated); fifth, the silent pauses caused by “have a blankin mind”, “don’t understand” and “information organization” last longer than the pausescaused by other factors; sixth, the participants make more pauses in Chinese-English CI thanin English-Chinese CI (both silent pauses and filled pauses); seventh, the total-length of thesilent pauses in Chinese-English CI is longer than the one in English-Chinese CI; eighth, theoccurring frequence of silent pauses and filled pauses is depended on the interpreter.
…………
Reference (omitted)
