Chapter 1 Introduction
1.1 Research Background
Writing is one of the most important ways of conveying information in dailylife. So English writing occupies an important position in English teaching in juniorhigh schools. The requirements of writing proposed by New English Curriculum(2011) for students in Junior Three are: As one of the basic language skills, writing is also a necessary content for testsin junior school. Combined with the curriculum, the criteria of composition gradingin the high school entrance examination puts forward requests that students shouldwrite the composition of 60-80 words according to the given cue words, pictures ortables, in which most points should be included, the vocabularies and sentences are mostly correct. The appropriate transitions and connective phrases can be used tomake the composition organized logically,and the main contents can be expressedclearly in limited time. When the standard for composition evaluation is used toevaluate the composition, it's clear that the quality of a written work mainly dependson the use of the vocabulary (Nation 2001). A composition is graded from thefluency, accuracy, idiomaticity of the expression and the construction of the content.In brief, the advanced requirements of English writing abilities, including fluent,accurate, idiomatic and logical use of vocabularies are raised for the students injunior school
…………
1.2 Purpose and Significance of the Research
During the study of Master of Education, the author contacted the concept ofthe lexical chunk. It refers to a multi-word unit which has fixed forms andprefabricated meaning. It is stored and remembered in the mind as a whole. It islarger than vocabulary, including phrases, idioms and even complete sentences aswell as single words. It's considered to be the unity of grammatical rules, semanticmeanings and pragmatic contexts (Wu & Wang 2002: 70) and can be extractedduring output any time without grammar rules analysis. Thus using lexical chunkscan reduce the risk of making vocabulary mistakes in writing English composition,improve the accuracy of using vocabularies and increase the competence ofconstruction in discourse organization in using language (Wu & Wang, 2002). So if students remember enough lexical chunks in their mind instead of vocabularieswithout any specific context and extract when writing, they may be more confidentin writing and write qualified compositions which include accurate vocabularies andsentences rather than Chinglish as well as appropriate transitions and connectivephrases so that they can improve their writing marks and competence.In this thesis, the author applies lexical chunks to writing teaching. Through aseries of teaching activities,including obtaining, remembering and applying lexicalchunks in writing, the author tries to establish an effective channel between languageinput and output by using lexical chunks and to investigate the validity of improvingEnglish writing scores and competence by using lexical chunks in Junior Three.Hopefully the results of the experiment can provide a new viewpoint to help thestudents solve the problems existing in writing and improve writing scores andcompetence in limited time.
……….
Chapter 2 Literature Review
2.1 The Definitions of Lexical Chunks
The importance of lexical chunks has won the approval, but the definition oflexical chunks has not been uniform in theory. Different researchers have alreadyused different terms to describe it.The concept of “lexical chunk” can be traced back to mid-20century, whichwas firstly raised by Becker. He proposes the concept of “idiosyncratic chunks”,which can be stored and remembered as a whole according to the features ofvocabulary. It's an appropriate combination offormulas, cliches, idioms allusions,slogans, and so forth (Becker 1975:111). He also suggests that people useready-made frameworks on which to hang the expression of our ideas, so that wedon't have to go through the labor of generating an utterance every time wcmt tosay something (Becker 1975:17).
………
2.2 The Classifications of Lexical Chunks
Like different definitions of the lexical chunk, different linguists classifylexical chunks from different perspectives. Because compared with otheroverlapping classifications, classification presented by Michael Lewis in 1993 isclearer and easier to understand by learners and this classification is reflected inteaching process of middle school (Deng 2011). In this paper, the classification madeby Lewis is adopted by the author.From the works of Lewis, The Lexical Approach (1993) and Implementing theLexical Approach (1997), it is concluded that lexical chunks are divided into fourmajor categories. They are words and poly-words,collocations or word partnerships,institutionalized utterances and sentence frames and heads. Words and poly-wordsIn his opinion, words are the largest and most familiar category contrary to traditional pedagogic ideas. They can be used all alone {Listen!/ Stop!) and they canalso be substituted in a fixed structure to express different meanings(CowW you tellme the way to the hospital/factory.).Poly-words are always very short 2- or 3-word phrases (Lewis 1997: 22),inwhich variability and divisibility are not allowed. So they are used as a individualwords, such as all the time, in the end, etc.
………
Chapter 3 Experimental Design...... 20
3.1 Hypotheses..... 20
3.2 Subjects..... 20
3.3 Instruments..... 21
3.4 The Process of the Experiment..... 24
Chapter 4 Data Analysis and Discussion..... 40
4.1 Analysis of Pre-questionnaire..... 40
4.2 Analysis of Post-questionnaire..... 43
4.3 Analysis of Pre-test and Post-test Writing..... 45
4.3.1 Analysis of Pre-test Writing..... 45
4.3.2 Analysis of Post-test Writing .....46
4.3.3 Analysis of Pre-test and Post-test Writing in EC..... 47
4.4 Analysis of Lexical Chunks Quantity .....48
4.5 The Correlation of the Quantity of Lexical Chunks ..... 51
4.6 Discussion..... 51
Chapter 5 Conclusions .....54
5.1 Major Findings..... 54
5.2 The Pedagogical Implications in Further Writing Teaching..... 56
5.3 Limitations.....57
Chapter 4 Data Analysis and Discussion
4,1 Analysis of Pre-questionnaire
Before the experiment, 85 copies of questionnaire are distributed to 43 studentsin EC and 42 students in CC. All the students finish it in 5 minutes individually andindependently. All the 85 copies are returned in the end. The following table brieflyshows the results. From Table 4-1. it's disappointing to conclude from Questions 1-3 that only 7%the students in EC and 19% of the students in CC are interested in English writing.Most of them, especially students in EC don't like writing in English although 56%of the students in EC and 55% of the students in CC think that English writing isvery important. As a result, only 9% of the students in both classes practice writingcompositions in English regularly and voluntarily.From Questions4-6, we can see 60% of the students in EC think their writinglevel is ordinary and 16% think they are in quite a low level, which are 8% and 4%higher than those in CC. 85% of the students in both classes find it not easy to writean English composition. So 16% of the students in EC and 12% of the students inCC lose confidence in English writing.
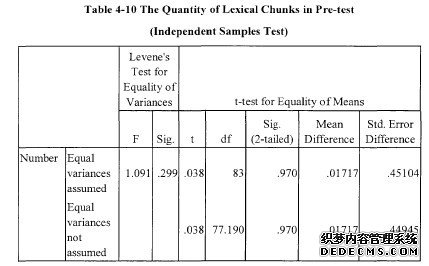
……….
Conclusion
In this study, the author applies lexical chunks to writing teaching. The primaryaim is to investigate the validity of improving English writing competence by usinglexical chunks in Junior Three. After four-month experiment and date analysis, threemajor findings are as fellow, which are the answers to the research question inChapter 3. From the account above, it's clear that lexical chunks consist of manymulti-word units or patterns that can be stored as a whole and easily obtained frommemory without restricted by grammar rules. The number of vocabulariesmemorized once is increased. With the design of kinds of activities in classroom,sufficient lexical chunks can be taken in. For the students, writing English becomeseasier because lexical chunks related to the writing topic can be used correctly whenthey write a composition after the training of lexical chunks recognition,consolidation and application in Writing. They don't have to think about the choiceof words, the grammatical correctness, the syntactic structure in writing process.
…………
Reference (omitted)
